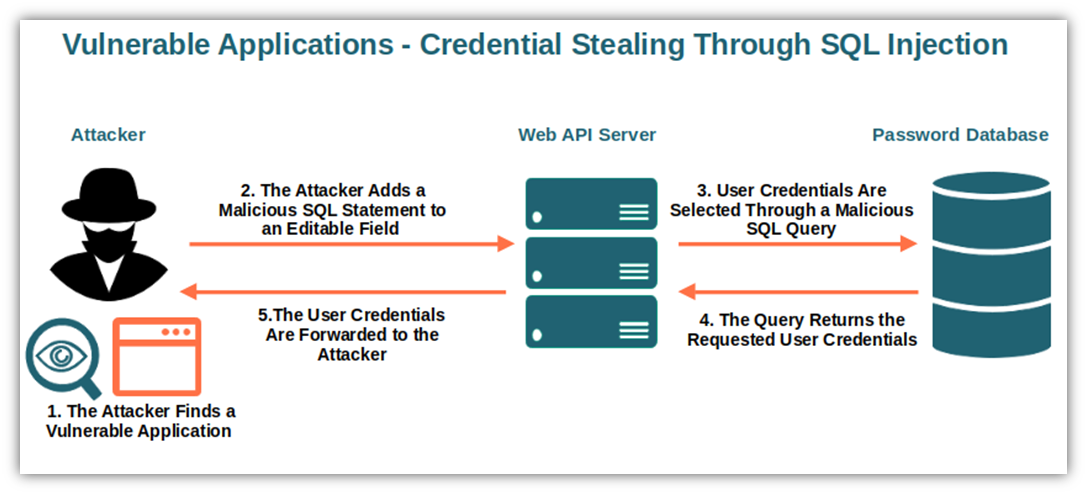
Credential theft is becoming a critical cybersecurity threat as cybercriminals refine their attacks, focusing less on flashy ransomware incidents and more on stealthy data breaches. Recent reports indicate that almost one in three cyber incidents in 2024 involved the compromise of user credentials, underscoring the escalating danger of credential theft. With growing sophistication, attackers exploit vulnerabilities and utilize phishing emails infused with infostealers to capture sensitive login information. This trend is alarming, especially considering that critical infrastructure organizations bore the brunt of these identity attacks, comprising 70% of all targeted efforts. As technology evolves, businesses must enhance their defenses, implementing proactive security measures to thwart the risk of credential theft and safeguard their digital assets.
The alarming rise in the appropriation of login details, often referred to as identity theft, highlights a troubling shift in the landscape of cybercrime. This form of attack, which primarily aims at obtaining sensitive authentication information, is closely tied to various modern threats such as phishing scams and the deployment of infostealer malware. As cyber attackers increasingly incorporate advanced tactics to infiltrate networks, businesses are facing an urgent call to bolster their cybersecurity posture. The exploitation of vulnerabilities within organizational systems presents a prime opportunity for malicious entities to thrive unnoticed. As we navigate through this evolving threat arena, understanding the implications of identity theft is crucial for carving a secure path forward.
Understanding Credential Theft in the Modern Landscape
Credential theft has emerged as one of the predominant cybersecurity threats in 2024, with attackers employing sophisticated methods to obtain sensitive login information. Unlike the more overt approach of ransomware attacks, which have seen a decline, credential theft operates under the radar, allowing cybercriminals to infiltrate systems without detection. Statistically, almost a third of all cyber incidents in the past year involved credential theft, highlighting the urgent need for organizations to enhance their security protocols. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services, the available identity gaps provide attackers with unique access points to exploit.
The rise in credential theft can primarily be attributed to the deployment of infostealers, which have proliferated in phishing emails. These malicious software programs are designed to extract login credentials directly from users’ devices, often without their knowledge. IBM X-Force’s report indicates an alarming 84 percent increase in emails delivering infostealers compared to previous years, underscoring a trend that is making identity attacks more feasible for cybercriminals. This tactic is especially concerning for critical infrastructure organizations, which accounted for a significant percentage of all attacks.
The Evolution of Cybersecurity Threats: Ransomware to Credential Theft
As cybercriminals adapt to emerging technologies and preventive measures, there has been a notable transition in the types of attacks employed. While ransomware attacks were once a preferred method for generating revenue, their decline in favor of credential theft signals a shift in the strategic approach of these actors. The pivot is likely spurred by advancements in detection technologies, which compel hackers to diversify their methods. Security experts are witnessing this change firsthand, as organizations increasingly experience data compromise rather than outright file encryption.
This evolution in methodology also reflects a growing sophistication among threat actors. With complex systems in place, especially in the hybrid cloud environment, criminal enterprises are finding creative ways to exploit vulnerabilities. Threat actors are investing in technology that allows them to automate phishing schemes, making it easier to launch large-scale attacks aimed at obtaining user credentials. The implications for businesses are severe, as the need to proactively guard against all forms of cyber threats becomes paramount in protecting sensitive data.
The Rise of Phishing Emails and Infostealers
Phishing emails have long been a dominant form of cyber attack, but their evolution continues to pose significant challenges for cybersecurity. According to IBM X-Force, the use of infostealers in phishing campaigns has spiked dramatically, with early data indicating a 180 percent increase in 2025 compared to the previous year. This alarming trend reveals not only the resourcefulness of cybercriminals but also the sheer volume of threats targeting unsuspecting victims. With attackers using artificial intelligence to craft convincing phishing emails, the risk of falling victim to these scams has never been higher.
The targeting is particularly pronounced in regions like Asia and North America, which account for nearly 60 percent of all cyber attacks monitored by IBM X-Force. In this digital landscape, the convergence of sophisticated phishing tactics and the rise of infostealers places immense pressure on organizations to implement robust security measures. These may include enhancing email security protocols and providing regular training for employees to recognize and respond to phishing attempts. Companies must prioritize real-time threat detection methods to combat these surging phishing attempts effectively.
Cybersecurity Protocols: Transitioning from Reactive to Proactive Measures
In light of the escalating threats associated with credential theft and phishing, businesses must reevaluate their cybersecurity frameworks. Traditionally, many organizations operated under a reactive approach; however, the changing dynamics of cyber threats necessitate a shift towards proactive security measures. This includes modernizing authentication management systems and addressing vulnerabilities associated with multi-factor authentication, which often serves as the first line of defense against unauthorized access.
Moreover, organizations are encouraged to conduct real-time threat hunting to unearth hidden dangers before they lead to significant breaches. Employing strategies such as continuous monitoring and regular security audits can help detect potential weaknesses that threat actors may exploit. With cybercriminals increasingly capable of infiltrating systems undetected, developing a proactive cybersecurity culture is essential in safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring continuity for business operations.
Identifying and Mitigating Identity Attacks
Identity attacks have become a significant concern in the realm of cybersecurity due to their potential to wreak havoc on businesses and individuals alike. These attacks can occur when cybercriminals manage to gain access to sensitive personal information, often leading to unauthorized account access and financial loss. The rise in credential theft has been particularly detrimental, with attackers utilizing stolen credentials to bypass security measures and orchestrate deeper breaches into organizational systems.
To mitigate the risk of identity attacks, organizations need to adopt comprehensive identity and access management solutions that provide granular control over user privileges. This involves implementing strong authentication practices, such as biometric verification and robust password policies. Furthermore, organizations should invest in user education and awareness training, helping employees recognize signs of identity theft and phishing attempts. By reinforcing security protocols and promoting a culture of vigilance, businesses can significantly decrease their susceptibility to identity attacks.
Impact of Cybersecurity on Critical Infrastructure
The impact of cybersecurity threats on critical infrastructure cannot be overstated. In 2024, organizations within this sector represented a staggering 70 percent of all attacks encountered by IBM X-Force. These statistics underscore the pressing need for enhanced cybersecurity measures, as breaches in critical infrastructure can lead to widespread consequences affecting national security. With attackers exploiting vulnerabilities in essential services, the stakes in securing these systems have never been higher.
To combat this reality, organizations must prioritize cybersecurity as a key component of their operational strategy. This includes conducting comprehensive risk assessments, as well as investing in advanced threat detection technologies that can monitor for suspicious activities in real-time. Furthermore, collaboration between private and public sectors becomes crucial in sharing threat intelligence and developing robust frameworks that protect critical infrastructure against an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Future Trends in Cybersecurity: Preparing for What’s Next
As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, staying ahead of emerging threats is critical for organizations aiming to protect sensitive information. Future trends suggest an ongoing rise in credential theft as cybercriminals delineate strategies for extracting valuable data with minimal risk. Companies will need to adapt by leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning technologies to improve their defenses against these prevalent threats.
Additionally, organizations should begin to anticipate the role that AI will play in both cyber offense and defense. While attackers utilize AI to automate the production of sophisticated phishing emails, defensively, businesses must explore AI-driven tools to detect anomalies and respond to security incidents more effectively. By embracing innovation and remaining agile in their cybersecurity strategies, organizations can better fortify their defenses in the face of an uncertain future.
The Role of Law Enforcement in Combating Cybercrime
Law enforcement agencies play an essential role in addressing the complexities of cybercrime, as evidenced by the heightened focus on combating credential theft and identity attacks. With the increasing frequency of these incidents, collaboration between law enforcement and organizations has become vital for swift incident response and recovery efforts. Agencies work closely with cybersecurity firms to share intelligence and develop best practices, facilitating improved defenses against cybercriminals.
Furthermore, proactive law enforcement initiatives, such as awareness campaigns and industry webinars, empower organizations to understand the current threat landscape. These efforts highlight the significance of compliance with regulations and adopting industry standards in cybersecurity. By fostering partnerships between law enforcement and the private sector, a unified front can be established to combat the illicit actions of cybercriminals and safeguard data integrity across industries.
Educating Employees: The First Line of Defense
In the battle against cybersecurity threats, an organization’s most valuable asset is often its employees. Education and training are critical components in establishing a strong security culture. Employees equipped with knowledge about the signs of phishing attempts, credential theft, and identity attacks can serve as the first line of defense against cybercrime. Regular training sessions, interactive workshops, and practical simulations can dramatically improve an organization’s resilience against such threats.
Moreover, fostering an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activity is key. Organizations should ensure that clear communication channels are established for employees to voice concerns or report potential threats without fear of backlash. By promoting awareness and cultivating a proactive security mindset, businesses can empower their workforce to contribute to a stronger overall cybersecurity posture.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is credential theft and how does it relate to cybersecurity threats?
Credential theft is the act of stealing login information, such as usernames and passwords, often through methods like phishing emails or infostealers. This rising form of cybercrime poses significant cybersecurity threats, as attackers can gain unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems, making it essential for businesses to adopt proactive security measures.
How are ransomware attacks connected to credential theft?
While ransomware attacks focus on encrypting data for ransom, increasing credential theft allows attackers to bypass traditional defenses and gain access to critical infrastructure. By stealing login credentials, cybercriminals can launch more targeted and effective ransomware attacks, leading to significant repercussions for organizations.
What role do phishing emails play in credential theft?
Phishing emails are a primary vector for credential theft, as they trick users into revealing sensitive information. The increase in phishing emails delivering infostealers is alarming, with IBM X-Force noting an 84 percent rise, indicating that attackers are leveraging these tactics to execute identity attacks and compromise accounts.
What are infostealers and how do they contribute to credential theft?
Infostealers are malicious software designed to extract sensitive information, including credentials, from a victim’s system. Their prevalence in phishing campaigns has surged, contributing significantly to credential theft incidents as attackers exploit vulnerabilities in users’ defenses.
How can businesses protect themselves from credential theft?
To safeguard against credential theft, businesses should implement strong authentication management practices, enhance multi-factor authentication protocols, and routinely conduct real-time threat hunting to identify vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of account takeovers.
What is the relationship between identity attacks and credential theft?
Identity attacks often rely on credential theft as a means to impersonate individuals, gaining unauthorized access to systems and data. Cybercriminals focus on stealing credentials to escalate these identity attacks, making it crucial for organizations to adopt robust security strategies.
Why are Asian and North American organizations more frequently targeted for credential theft?
Asia and North America account for nearly 60 percent of credential theft incidents, likely due to the concentration of valuable data and the presence of complex hybrid cloud environments that present numerous access points for attackers.
What proactive measures can organizations take to combat credential theft?
Organizations can combat credential theft by modernizing their authentication systems, strengthening multi-factor authentication, conducting regular security assessments, and investing in advanced threat detection technologies to identify and mitigate risks before an attack occurs.
| Key Points | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| Shift in Cybercrime Tactics | Cybercriminals are increasingly focusing on credential theft instead of higher-profile ransomware attacks. | |
| Increase in Infostealer Emails | Emails delivering infostealers rose by 84% in 2024 compared to 2023, indicating a shift toward more subtle exploitation. | |
| Credential Theft Prevalence | Almost one in three cyber incidents resulted in credential theft, illustrating a growing focus on accessing and monetizing login information. | |
| Attacks on Critical Infrastructure | 70% of attacks addressed by IBM X-Force targeted critical infrastructure, with many exploiting known vulnerabilities. | |
| Shift Away from Data Encryption | More cybercriminals (18%) are opting to steal data instead of encrypting it (11%), requiring faster exit strategies due to improved detection and law enforcement. | |
| Proactive Defense Recommendations | Businesses need to modernize authentication management and conduct real-time threat hunting to address vulnerabilities. | |
| Geographical Insights | Asia and North America comprise nearly 60% of all attacks, with Asia sustaining 34% and North America 24%. | |
| Upcoming Webinar | A webinar discussing these findings is scheduled for April 22nd at 11am ET. | |
Summary
Credential theft has emerged as a dominant threat in the cybersecurity landscape, with nearly one-third of cyber incidents in 2024 being attributed to this method. As cybercriminals increasingly rely on sophisticated tactics such as infostealer distribution through phishing emails, companies must adapt by enhancing their security measures. The reported 84% increase in credential theft-related emails highlights the urgency for businesses to transition from reactive security strategies towards proactive ones. By modernizing authentication processes and conducting real-time threat hunts, organizations can better defend against the growing wave of credential theft attacks.