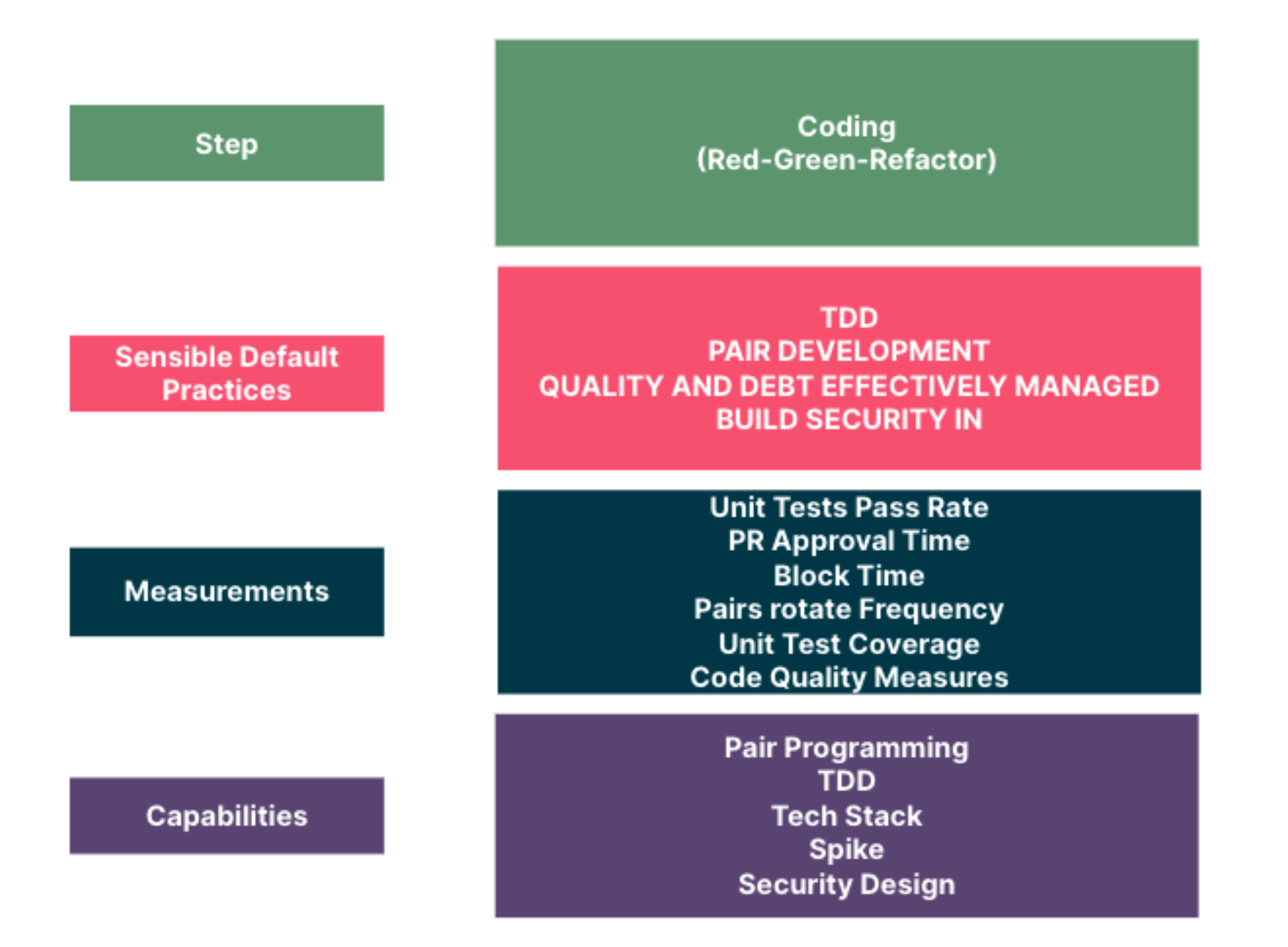
Engineering productivity is a critical focus for software development organizations, particularly as they strive to overcome common pitfalls such as productivity blind spots and inefficient workflows. Enhancing engineering productivity involves more than just tracking productivity metrics; it requires a holistic view that leverages data-driven insights to identify areas for improvement and foster effective engineering change management. Organizations face various challenges, including duplicate efforts, unrealistic deadlines, and burnout among team members, all of which can hinder overall efficiency. To achieve sustainable improvement, teams must embrace iterative change processes that facilitate ongoing assessment and adaptation. By integrating empirical data with a culture of continuous growth, engineering teams can transform obstacles into opportunities and unlock their full potential in delivering high-quality software solutions.
In the realm of software development, the quest for increased efficiency and effectiveness often leads to a keen interest in enhancing engineering output. This pursuit, often referred to using terms such as productivity enhancement and change management strategies, emphasizes the importance of effective team dynamics and informed decision-making. The role of robust productivity indicators cannot be overstated; however, they must be coupled with a deeper understanding of team behavior and contextual factors that influence performance. Continuous improvement through adaptive management techniques is essential, allowing engineering teams to address both ongoing challenges and emerging opportunities. Overall, the journey towards improved operational effectiveness in engineering demands a comprehensive approach that balances quantitative analysis with qualitative insights.
Understanding Engineering Productivity Challenges
Engineering teams today face significant challenges that impede their productivity, leading to issues such as burnout, misalignment with business goals, and inefficient processes. Identifying the root causes of these difficulties often requires more than mere measurement; it necessitates a comprehensive understanding of team behaviors and underlying dynamics. Productivity metrics, while useful, might not capture the nuances of how teams interact with one another, resulting in blind spots that can hinder effective change management.
For example, teams might be bogged down by excessive meetings or unclear roles within projects, resulting in duplicated efforts and project delays. Understanding these dynamics typically requires open dialogue with team members rather than simply reviewing productivity stats. To adequately develop strategies for improving engineering productivity, organizations must bridge the gap between data insights and human factors.
The Dangers of Solely Relying on Metrics
While metrics are critical for tracking productivity, relying on them to drive performance improvements can lead to misguided initiatives. For instance, an analysis that shows a team is behind schedule may prompt leadership to impose stricter deadlines or increased oversight without addressing the root causes, such as inadequate resources or poor communication with stakeholders. This reactive approach can foster a culture of blame and disengagement.
Moreover, hidden costs associated with misdiagnosing performance issues include diminished team morale and heightened frustration over unrealistic expectations. To effectively utilize productivity metrics, organizations should prioritize establishing an environment where team members feel safe to share insights about challenges they’re encountering, allowing for a more accurate assessment of areas for improvement.
Implementing Iterative Change Management for Continuous Improvement
Iterative change management refers to a systematic approach to implementing changes that are regularly reviewed and adjusted based on ongoing feedback and data-driven insights. Unlike traditional change management, which may adopt a one-size-fits-all protocol, iterative management promotes flexibility and responsiveness, encouraging engineering teams to continuously refine their processes and enhance productivity. This approach is crucial in today’s fast-paced engineering environments, where needs and conditions can shift rapidly.
To effectively implement iterative change management, organizations must equip their teams with the necessary tools, support, and autonomy to experiment with process modifications. By integrating feedback loops into the workflow, teams can identify action areas that genuinely improve productivity and collaboration. This consistent reassessment fosters a culture of innovation, where continuous improvement becomes part of the daily routine.
The Role of Data-Driven Insights in Engineering Productivity
Incorporating data-driven insights into engineering practices provides a robust framework for understanding productivity metrics and addressing performance issues. These insights should not only surface existing problems but also illuminate the context in which they arise, helping teams to formulate actionable strategies. By leveraging analytics effectively, teams can develop tailored action plans that align with their specific operational realities, targeting areas that can boost output and reduce inefficiencies.
However, insights alone are inadequate for driving change. It is essential to complement data analysis with hands-on change management strategies. Teams must be engaged in interpreting insights and encouraged to participate in the decision-making process. This collaborative approach ensures that changes are relevant and welcomed, enhancing the likelihood of successful implementation.
Change Enablement: Bridging the Gap in Engineering
Change enablement palys a pivotal role in fostering an environment where engineering teams can thrive amidst transformation. By marrying data analytics with effective change strategies, organizations can better equip their teams to identify improvement opportunities and execute necessary changes efficiently. The key lies in creating a shared understanding of the ‘why’ behind each metric, which empowers engineers to take ownership of their productivity outcomes.
This holistic model acknowledges that successful productivity improvement is not purely a technical challenge but also a social one. Creating an open culture, where opinions and insights are valued, can lead to more vibrant conversations and more innovative solutions. Ultimately, bridging this gap not only enhances productivity metrics but also increases team morale and job satisfaction.
Strategies for Improving Engineering Productivity
To effectively enhance engineering productivity, organizations must adopt a comprehensive strategy that involves both process improvement and cultural shifts. This includes actively soliciting input from teams on obstacles they face and implementing looping mechanisms for regular feedback. By engaging team members in the solution-finding process, leaders can foster a sense of ownership over their work and drive meaningful change.
Moreover, utilizing data-driven insights to track performance over time allows teams to not only understand what changes are effective but also to maintain ongoing dialogues about performance goals and measures. Regular workshops focused on metric analysis and team feedback can help identify trends, challenges, and opportunities for further improvement, ensuring that productivity enhancements remain a dynamic and evolving process.
The Importance of Collaboration in Change Management
Collaboration is paramount in change management initiatives aimed at improving engineering productivity. Successful change requires buy-in from engineers at all levels—when teams understand and are engaged in the process, they are more likely to embrace new methods and strategies. Encouraging team collaboration, both formally (via performance reviews and meetings) and informally, creates an open line of communication that can significantly decrease the friction often associated with adopting changes.
Moreover, data should serve as a backdrop for conversations rather than the focal point. Leadership can use productivity metrics to highlight trends but must also emphasize the stories behind the numbers. Creating channels for teams to discuss their experiences related to productivity blinds spots can capture critical insights that data alone may miss, thus informing a more effective and inclusive change process.
Challenges of Change Management in Large Organizations
Change management in larger engineering organizations involves navigating intricate hierarchies and diverse stakeholder expectations. As changes ripple through the organization, misalignment can occur, creating resistance and frustration. Larger teams may struggle with establishing a unified vision for productivity improvement since disparate departments or teams might have different priorities, making consensus difficult. Engaging stakeholders early and often in the change process can mitigate these risks.
By fostering a culture where all employees feel their voices are heard, organizations can better facilitate collaboration and commitment to a shared goal. It is vital for leaders to continuously provide clarity on the ‘why’ of changes. This shared understanding not only aids in aligning objectives across teams but also eases the adoption of new processes essential for enhancing productivity.
Future Trends in Engineering Productivity and Change Management
As industries evolve, the understanding and management of productivity are likely to continue to shift. Engineering teams are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to provide deeper insights into performance metrics and productivity blockers. With the advent of these technologies, change management strategies must evolve to better integrate these sophisticated analytics tools into day-to-day operations.
Anticipating future trends also means being proactive about continuous learning and adapting best practices from other sectors. Organizations that look beyond engineering for change enablement models will be ahead of the curve, enabling them to implement successful strategies that not only boost productivity metrics but also foster an engaging work environment for engineers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are common challenges in improving engineering productivity?
Improving engineering productivity can be hindered by challenges such as productivity blind spots, duplicate efforts, unattainable deadlines, and burnout. Effective engineering productivity enhancement involves not just measurement but also understanding team dynamics and engaging in change management.
Why is relying solely on productivity metrics risky for engineering teams?
Relying solely on productivity metrics can be risky as it may lead to misunderstanding the root causes of performance issues. For example, metrics might show extended completion times due to complex work, yet they may not reveal underlying problems like poor team coordination or communication issues that require direct engagement to understand fully.
What is iterative change management and how does it improve engineering productivity?
Iterative change management is a continuous process that focuses on identifying, implementing, and reassessing changes required to drive engineering productivity improvements. This approach emphasizes using data-driven insights to find valuable change opportunities and empower teams to adapt as their systems and challenges evolve.
How do data-driven insights contribute to effective engineering change management?
Data-driven insights help engineering teams by providing context and identifying issues through metrics. However, effective change management combines these insights with hands-on approaches, ensuring teams understand the ‘why’ behind changes and are actively engaged in problem-solving, leading to more sustainable productivity improvements.
What advice can engineering leaders follow to foster change management effectively?
Engineering leaders should recognize that improving productivity requires addressing both technical and social aspects. Engaging teams in understanding metrics and involving them in the change process not only fosters ownership but also enhances the likelihood of successful adoption of new practices.
How can other industries benefit from a data-driven change enablement model similar to engineering?
Other industries, like sales, have successfully utilized data-driven change enablement models for years by combining metrics with team insights. By understanding the context behind the data and engaging teams in identifying solutions, organizations in various sectors can overcome bottlenecks and enhance overall performance.
What role does communication play in improving engineering productivity?
Effective communication is vital in improving engineering productivity as it enables teams to share insights, clarify expectations, and understand the intricacies of challenges faced. Regular discussions about productivity metrics help in uncovering blind spots that metrics alone cannot reveal, ensuring that teams work collaboratively towards solutions.
What hidden costs can hinder engineering productivity that are not visible through metrics?
Hidden costs that can hinder engineering productivity often include wasted time due to poor coordination, duplicated efforts across teams, and burnout from unrealistic deadlines. These issues typically require direct engagement and conversation with teams to identify and address effectively.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Productivity Blind Spots | Unrecognized issues that hinder team performance, often hidden behind metrics. |
| Duplicate Efforts | Redundant work caused by insufficient communication and project coordination. |
| Unattainable Deadlines | Deadlines that do not consider project complexity, leading to team burnout. |
| Burnout | Emotional and physical exhaustion stemming from excessive workload and pressure. |
| Hidden Costs | Indirect costs associated with inefficient processes and poor management practices. |
| Iterative Change Management | A continuous process of assessing and implementing changes based on team feedback. |
| Data-Driven Insights | Using metrics in conjunction with contextual understanding to drive productivity improvements. |
| Team Engagement | Involving teams in the change process leads to better adoption of new practices. |
Summary
Engineering productivity is often compromised by several key challenges that impede progress. To truly enhance engineering productivity, organizations must recognize the importance of not only measuring performance but also understanding the context behind the numbers. Addressing the human factors and fostering team involvement in change initiatives can lead to significant improvements in productivity. Ultimately, a holistic approach that combines data-driven insights with active change management is essential for overcoming obstacles and driving sustainable growth within engineering teams.